We must agree that, in the manufacturing world, there are a lot of abbreviations and acronyms. While they can be confusing for newcomers, the real benefit comes from understanding how these terms are connected and what they bring to the production plant and employees.
Almost a “must” for modern manufacturing, ERP, MES, and APS systems promise valuable improvements and benefits, such as improving efficiency, optimizing production, and, in the end—staying competitive.
But first, let’s look at a simple example of ERP, MES, and APS to understand what they basically are.
What is ERP?
Enterprise Resource Planning, or simply ERP, is a system that plans and tracks everything a company has and does. For example, imagine a factory that produces tables. We can use ERP to:
- Track how much wood, nails, and glue we have in stock.
- Plan how many tables we need to produce next week based on customer orders.
- Monitor costs for materials, workers, and machine maintenance.
- Coordinate with the purchasing department (to buy materials) and the sales department (to deliver finished tables to customers).
In simple terms, ERP handles high-level planning—what the factory needs to do and what resources are required—ensuring that all departments (sales, finance, production, etc.) are aligned and working together. Since ERP integrates different business functions into one system, it provides a bird’s-eye view of the company, helping to make better plans and decisions.
What is MES?
The Manufacturing Execution System, or simply MES, monitors what is happening on the shop floor during production by collecting real-time data from machines and workers to ensure everything runs smoothly. In our imaginary table factory, MES can help us:
- Track which materials are being used and how many tables are currently being produced.
- Monitor machines—checking if they are running correctly, at what speed, and whether there are any issues.
- Collect real-time data, such as how many tables have been completed so far.
- Alert the team immediately if a machine breaks down.
Basically, MES focuses on controlling operations in real-time on the shop floor. It provides visibility into how production is running, allowing us to make decisions and react before problems occur.
What is APS?
The Advanced Planning and Scheduling system, or APS, focuses on detailed planning and optimization. It acts as a bridge between ERP and MES. APS uses data from ERP to generate production plans and forwards them to MES for execution and monitoring. In our example of a table factory, APS helps us:
- Decide the order in which machines should work on different table models to meet delivery deadlines.
- Estimate how many workers and materials are needed for each table model and when they should be ready.
- Quickly adjust the plan if a machine breaks down, ensuring minimal delays.
APS focuses on smart planning—how to make the best use of resources and time to plan, schedule, and optimize production processes for the best results at minimal cost.
For example, our solution – Qlector LEAP, is an APS but AI-based, meaning it uses machine learning algorithms to provide manufacturing facilities with comprehensive insights, forecasting abilities, and advanced production optimization.
Unlike MES, which works on the execution level to monitor and handle production processes, APS operates at a higher level, developing plans and schedules based on data from ERP, such as available resources and customer demands.
But How Do They Work Together?
- ERP handles high-level planning: “We need to produce 500 tables this week.”
- APS creates a detailed schedule: “Machine A will make model X in the morning and model Y in the afternoon.”
- MES monitors real-time production: “Machine A is currently making model X and will finish in 2 hours.”
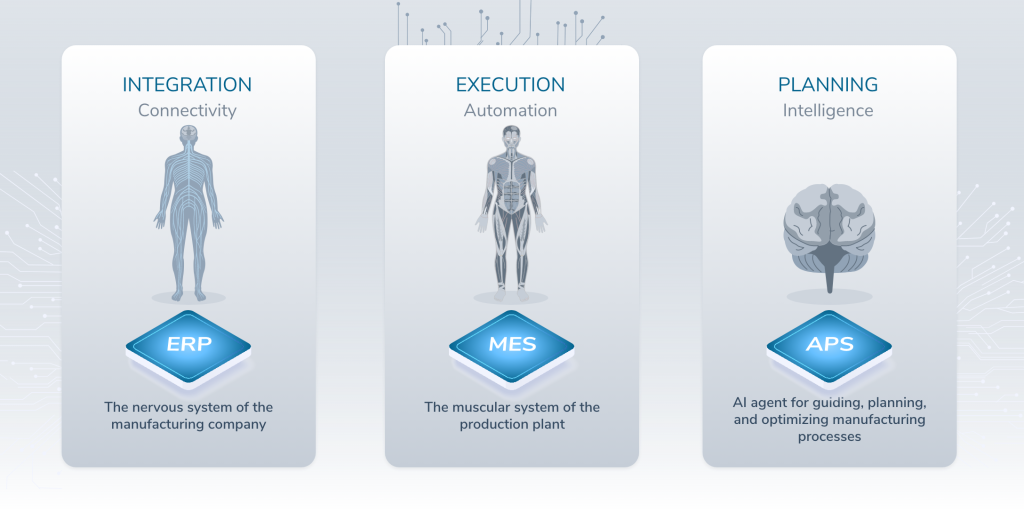
For an even better explanation, we can draw an analogy with the human body:
The nervous system represents connectivity and coordination, analogous to ERP. Just as the nervous system links all parts of the body, ERP integrates various departments within a business, ensuring everything is aligned.
The brain represents intelligence and decision-making, aligning with APS, which interprets data and generates optimized production schedules.
The muscular system represents physical actions and execution processes, much like MES, which monitors and controls real-time activities on the shop floor—ensuring the “muscles” (machines and workers) are functioning smoothly.
In Summary
ERP is excellent for overall business management but struggles with shop-floor-specific tasks. MES excels at real-time execution but lacks strong planning and scheduling features.
APS provides powerful planning and optimization but depends heavily on good data and integration.
Which of these systems you need depends on your company’s goals, needs, and budget. Combining them provides greater possibilities, as they complement each other to create smooth and efficient processes.
However, not all APS solutions are the same. The ones that belong to the next generation of powerful manufacturing tools are AI-based.
How can you benefit from AI-based APS?
AI-based APS solutions, such as Qlector Leap, harness the power of machine learning algorithms to analyze historical data, predict shop floor events, and adapt to changes in production processes.
These solutions excel in managing complex and dynamic manufacturing environments, offering greater robustness in handling unexpected changes and seamless integration with ERP systems.
They provide valuable insights into factory operations and simulate future production flows for accurate predictions. By adapting to real-world data, they function as an AI control tower for manufacturing, boosting efficiency, simplifying processes, and making them more transparent and predictable than ever before.
Or as our colleague said, aligning with the aforementioned comparison to the human body: ERP is the nervous system of the company, MES represents the muscles, and LEAP helps to move everything.
If you are interested in how, for example, an AI-based APS solution can successfully enrich and extend one of the most renowned yet complex enterprise resource planning software systems – SAP, read our blog here.
You can always book your FREE 30-minute consultation to discover the value AI-based APS can bring to your company.